The intent of this article is to inform the community that frequents this area about the existence of figures unprofessional, which, over time, have contributed to spreading a distorted view of the dynamics that regulate the network. We want to clarify these issues and to be made for curiosity.
The Backbone
Internet backbone carries data through (literally the "backbone") that are fiber optic cables placed throughout the country.
Internet Exchange Point
The highway intersections allow the sorting of traffic flow in different directions. Thanks to them all highways are interconnected. On the Internet this is done in the Internet Exchange Point (IXP), neuralgic facilities that allow you to keep up the speed and efficiency of the Internet as well as to contain costs. The main IXP "public" assets in Italy are 6 and each is identified by a code (Mnemonic).
Most important IXP in Italy are the MIX of MIlan and NaMeX Rome in which there are various operators such as Fastweb, Lottomatica, Telecom Italy, Tiscali, Vodafone, Wind.
The IXP were created by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) who are the managers of internet connectivity. In arriving IXP the backbone of all ISPs that have agreed their presence within these structures.
In the absence of the IXP the transfer rate of data would be far higher, inefficient and very expensive. Returning to our analogy would be like to have so many highways not connected.
There are thousands of IXPs in the world and they are all interconnected to form a global network for the exchange of data between operators free internet connectivity worldwide. This is a partial list of the main European IXP they are connected to the server. .
| Città | Mnemonic | |
| Vienna | VIX | |
| Bruxelles | BNIX | |
| Parigi | SFINX | |
| Parigi | FreeIX | |
| Francoforte | DE-CIX | |
| Francoforte | KleyRex | |
| Milano | MIX | |
| Roma | NaMeX | |
| Torino | TOP-IX | |
| Amsterdam | AMS-IX | |
| Amsterdam | NL-ix | |
| Varsavia | PLIX | |
| Londra | LINX | |
| Praga | NIX.CZ | |
| Madrid | ESPANIX | |
| Zurigo | SwissIX | |
| Zurigo | TIX |
Being interconnected to each other IXP IXP, have access to one of them allows an optimal routing with the global network. Have access to more than one IXP it allows players to have more options in the event of faults in the network or high traffic. For example, if the transition Turin -> Zurich is congested, the data will take an alternative route as Milan -> Zurich.
The telephone exchanges
The telephone exchanges are a bit like a motorway which gives us access to the city network to reach our final destination. Similarly, the telephone exchanges dealing with transport data from the last stretch up the backbone ale cabins that are close to your home or your office.
The Webfarm
A web farm, also known as data center, is the structure where they placed servers that host Internet content. Websites, software games, videos, emails, social networks ... all content accessible from the Internet are stored in these large structures connected to the main backbone network and IXP handles traffic both inbound and outbound. We, for example, we are present in a web farm located in Germany.
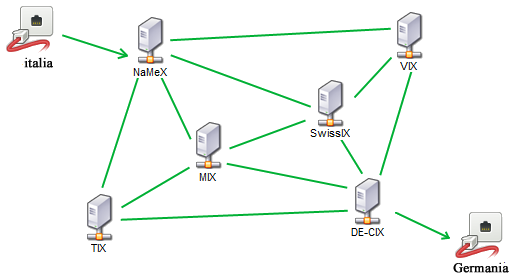
The image above gives an idea of the interconnections that exist between the IXP. Thanks to this structure packets can arrive at your destination by taking different paths.
The examples that I have given are purely theoretical and simplified. Each ISP has it own rules, networks, agreements with other IXPs and ISPs and structures that can lead us to make different paths.
The deception of some individuals not professionals
The ping is the time, expressed in milliseconds, it takes for a packet to reach a device in the network. Have 1,000 ping means being 1 second delay in the connection.
The lag, better known as latency, is the phenomenon that occurs when there is a high delay, due to a ping high, in the connection. In a normal navigation on websites this phenomenon is generally not perceived. It instead feels very in online games and voice communications / video. They occur in fact shots of the images or dropouts in or, in severe cases, connection errors.
There are providers that they have no problem in ensuring their customers a low ping and also the certainty of the absence of lag. They are performed sounding slogans such as "lag free", "low ping", "Lowest Ping". The reality is that those who ensures low ping or services without lag knows little or nothing about how a network or simply are doing false advertising.
Any provider in the world can guarantee a low ping nor the lack of lag. This is because the exchange of data between the server (which hosts the service that you want to use) and the client (your PC or device) is reciprocal. If you are connected wirelessly with UMTS, GPRS, WiFi (technologies subject to the constraint of signal reception), if you are away from the central office or if his ISP (the company that provides you with the Internet) has the congested lines, there is no provider that can get you a low ping. Only in a direct connect client-server you can talk about ping zero and no lag. No provider, however, can guarantee it as would install the server directly to your home.
Inspired more by our usual analogy, ensure low ping and no lag as would ensure no traffic on the highway. This is not possible even in the most advanced transport system. Just as in the network, which has much in common with a motorway, they may experience delays, accidents and maintenance.
For a more clear and complete you need to know that everything depends solely on your telephone or by those who have agreements with it.
Common problems in the network
Here are some of the common problems that cause the increase in the table and the consequent presence of lag.
Routing is not optimal
ISPs are routing data in the shortest and fastest route between the IXP and destination (optimal situation for a low ping). In some cases, however, it can happen that the traffic will not be routed in the shortest route but in the less used to avoid overloading parts of the network in the hours to more traffic. In these moments it is preferred to sacrifice a few milliseconds of the table in order to maintain a functional connection, and reliable. In the low-cost ISP this does not occur as it does not have bandwidth and accesses to the IXP sufficient for all their customers. When this occurs, not only the ping gets up but the connection becomes unstable because the network is saturated.
Last mile
Output from switching to urban network much slower and definitely more prone to problems and traffic. The telephone exchanges have the same type of problem. These in fact define the transition of data from fast backbone to slower copper connections that arrive in our offices and homes. Most common is not yet reached by the optical fiber or even not reached by ADSL technology, therefore much of the speed and efficiency accumulated in the backbone is lost. The loss of signal strength is closely related to the distance from the telephone: the so-called last mile.
Traffic and events of force majeure
Occasionally there might be congestion on the network caused by heavy traffic. In other cases may be due to maintenance, ddos attacks or natural events. In these moments navigation could give some problems more or less evident depending on the case.

